Montana’s Native Tapestry: A Guide to the Reservations that Shape the State
Montana’s Native Tapestry: A Guide to the Reservations that Shape the State
Montana, with its sprawling landscapes and rugged beauty, is a place where history whispers through the wind. But beneath the surface of its iconic mountains and rolling plains lies a rich tapestry woven by the hands of its original inhabitants – the Native American tribes who have called this land home for centuries.
These tribes, with their distinct cultures, languages, and traditions, have shaped Montana’s identity and continue to play a vital role in the state’s vibrant fabric. But understanding their presence requires a deeper dive – a journey across the map of Montana’s reservations.
Related Articles: Montana’s Native Tapestry: A Guide to the Reservations that Shape the State
- Scottsdale’s Hidden History: Uncovering The Tribes Who Shaped The Valley
- Unveiling California's Native American Heritage: Discover Lost Tribes and Ancient Wisdom
- Unveiling The Tapestry Of Native Lands: A Guide To US Reservations
- Living Large: A Look Inside South Dakota’s Biggest Reservation
- Unveil the Hidden Gems: Exploring the Vibrant Native American Tribes of Washington State
A Map Unfolding: Exploring the Reservations of Montana
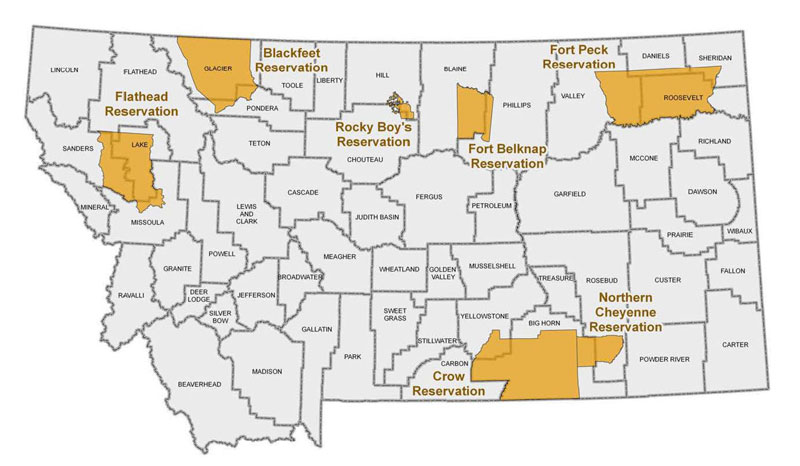
Montana is home to seven federally recognized tribes, each with its own reservation, a designated area of land set aside for their governance and self-determination. These reservations, like islands of sovereignty within the state, offer a glimpse into the enduring spirit of Native American communities and their connection to the land.
1. The Blackfeet Nation: Guardians of the Glacier
The Blackfeet Nation, whose name translates to "people of the black feet," occupies the largest reservation in Montana, encompassing a vast swathe of land in the northwest. They’re known for their deep connection to the majestic Glacier National Park, a place that holds sacred significance for the Blackfeet people. Their history, steeped in tradition and resilience, is evident in their cultural practices, like the Sun Dance, and their vibrant arts and crafts.
2. The Fort Belknap Indian Community: Where Two Tribes Stand United
The Fort Belknap Indian Community, located in north-central Montana, is unique in its composition, housing both the Assiniboine and Gros Ventre tribes. The Assiniboine, known as the "Stone People," were renowned hunters and warriors, while the Gros Ventre, meaning "belly-button people," were skilled farmers and artisans. Their shared history and resilience have forged a strong bond between these two tribes, creating a rich cultural tapestry on the Fort Belknap reservation.
3. The Crow Nation: Keepers of the Little Bighorn
The Crow Nation, residing in the southeastern part of Montana, holds a prominent place in American history. Their land is forever linked to the Battle of Little Bighorn, where they played a crucial role alongside the Lakota and Cheyenne tribes. The Crow Nation, known for their horsemanship and military prowess, have preserved their traditions and language, offering a glimpse into a vibrant and enduring culture.

4. The Flathead Nation: Guardians of the Bitterroot Valley
The Flathead Nation, residing in western Montana, has a deep connection to the Bitterroot Valley, a region they’ve called home for centuries. Their name, "Salish," meaning "people of the Salish language," reflects their strong cultural identity. The Flathead Nation is known for its skilled craftspeople, particularly in beadwork, and its commitment to preserving its language and traditions.
5. The Northern Cheyenne Tribe: A Journey of Resilience
The Northern Cheyenne Tribe, originally from the Great Plains, found refuge in Montana after being forcibly relocated from their ancestral home in the 1870s. Their reservation, nestled in the southeast corner of the state, reflects their spirit of resilience and adaptation. The Northern Cheyenne Tribe is known for its vibrant cultural traditions, including the Sun Dance and its powerful storytelling legacy.
6. The Rocky Boy’s Indian Reservation: A Blend of Cultures

The Rocky Boy’s Indian Reservation, located in north-central Montana, is home to a unique blend of cultures. It was established for the Chippewa Cree Tribe, who migrated west in the 19th century. However, the reservation also includes members of the Assiniboine Tribe, creating a diverse community with a rich cultural heritage.
7. The Confederated Salish and Kootenai Tribes: Guardians of the Flathead Lake
The Confederated Salish and Kootenai Tribes, residing in western Montana, hold a special place in the state’s history. Their reservation, encompassing the scenic Flathead Lake, is a testament to their enduring connection to the land. The Salish and Kootenai tribes, with their distinct languages and traditions, have worked tirelessly to preserve their cultural heritage and ensure its future.
Beyond the Map: Understanding the Importance of Reservations
The reservations of Montana are more than just geographical locations; they represent the heart and soul of the state’s Native American communities. They are spaces of self-governance, cultural preservation, and economic development. These reservations are vital to the well-being of Native Americans in Montana, providing a platform for them to maintain their traditions, languages, and cultural identities.

A Call to Action: Respect, Recognition, and Understanding
Understanding the reservations of Montana is not just about knowing where they are on a map; it’s about acknowledging the history, culture, and resilience of the Native American tribes who call them home. It’s about recognizing their unique sovereignty and respecting their right to self-determination.
Moving Forward: A Shared Future
The future of Montana’s reservations is intertwined with the future of the state itself. As we move forward, it’s crucial to foster a spirit of collaboration and mutual respect. By working together, we can build a future where the traditions and cultures of Montana’s Native American tribes are honored, celebrated, and passed down for generations to come.
FAQ: Exploring the Reservations of Montana
Q: What is the significance of the reservations for the Native American tribes?
A: The reservations are vital for the tribes as they provide a space for self-governance, cultural preservation, and economic development. They allow the tribes to maintain their traditions, languages, and cultural identities.
Q: How can I learn more about the history and culture of the tribes?
A: You can visit the tribal museums and cultural centers located on the reservations. You can also attend cultural events and festivals organized by the tribes.
Q: What are some of the challenges faced by the reservations?
A: The reservations face challenges such as poverty, unemployment, and lack of access to healthcare and education. However, the tribes are working tirelessly to address these challenges and improve the lives of their members.
Q: How can I support the tribes and their efforts?
A: You can support the tribes by visiting their reservations, purchasing their crafts and artwork, and advocating for their rights and interests. You can also donate to organizations that support Native American communities.
Q: What is the future of the reservations?
A: The future of the reservations is bright. The tribes are working to develop their economies, preserve their cultural heritage, and improve the lives of their members. By fostering a spirit of collaboration and mutual respect, we can ensure a future where the traditions and cultures of Montana’s Native American tribes are honored, celebrated, and passed down for generations to come.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Montana’s Native Tapestry: A Guide to the Reservations that Shape the State. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!