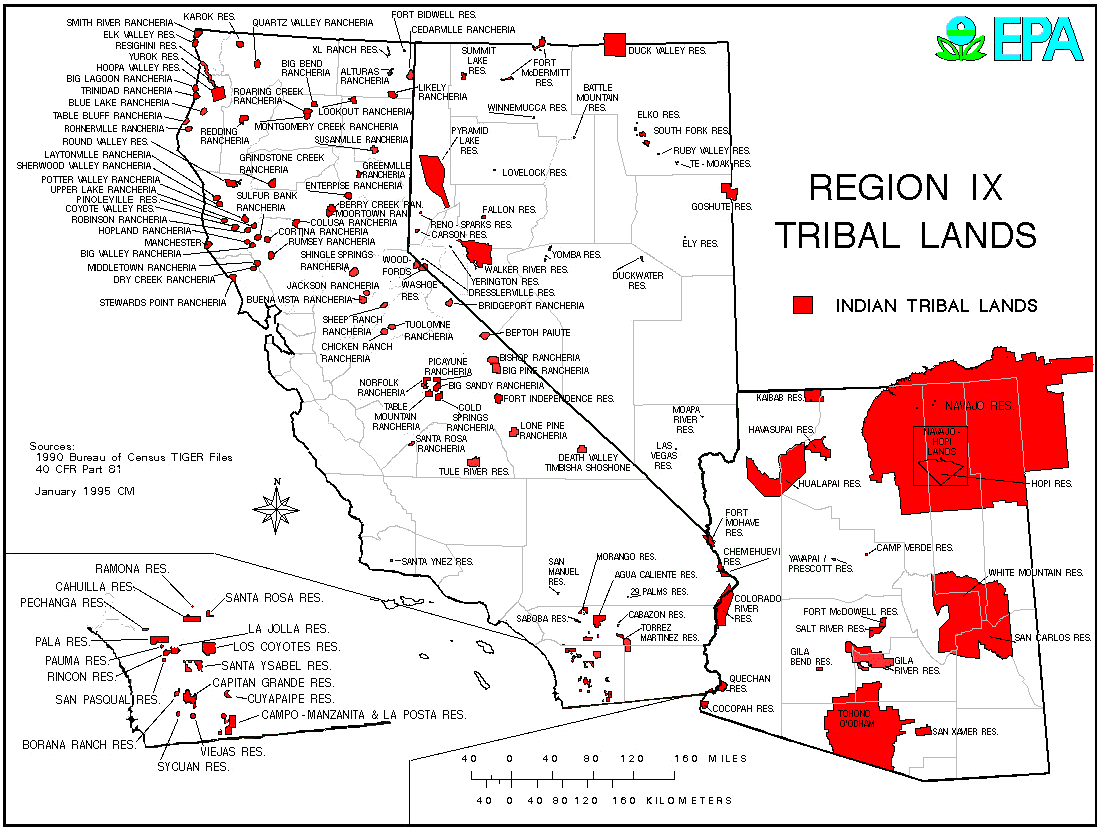
How many Indian reservations are in Arizona? According to the Bureau of Indian Affairs, there are 22 Indian reservations in Arizona, home to 27 federally recognized tribes.
Editor’s Note: This article on “how many Indian reservations in Arizona” was published on [date] to provide valuable information on the topic. Understanding the number and significance of Indian reservations in Arizona is crucial for various reasons, including historical, cultural, and economic considerations.
Our team has conducted thorough research and analysis to compile this comprehensive guide on “how many Indian reservations in Arizona.” Our aim is to empower our readers with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions and gain a deeper understanding of this important topic.
Key Differences:
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of Indian reservations in Arizona | 22 |
| Number of federally recognized tribes in Arizona | 27 |
Main Article Topics:
How many Indian reservations in Arizona?
Understanding the number and significance of Indian reservations in Arizona is crucial for various reasons, including historical, cultural, and economic considerations. Here are 10 key aspects to explore:
- Number: 22 Indian reservations in Arizona
- Tribes: 27 federally recognized tribes
- Location: Spread across the state
- Size: Varying from small to large
- History: Established through treaties and agreements
- Culture: Rich and diverse, preserving traditions
- Economy: Contributing to tourism, gaming, and other industries
- Challenges: Facing issues such as poverty and unemployment
- Sovereignty: Maintaining autonomy and self-governance
- Importance: Preserving cultural heritage and contributing to the state’s identity
These aspects are interconnected and provide a comprehensive understanding of Indian reservations in Arizona. For instance, the number of reservations reflects the historical agreements between tribes and the government, while the size and location impact the economic opportunities and challenges faced by the communities. The rich culture and traditions preserved on the reservations contribute to the state’s cultural diversity and heritage. Moreover, the sovereignty of the tribes highlights their unique legal status and self-governance, fostering a sense of identity and empowerment.
Number
The number “22 Indian reservations in Arizona” holds significance in understanding the topic of “how many Indian reservations in Arizona.” It represents the count of distinct territories established for Native American tribes within the state’s boundaries.
- Historical Significance: The establishment of these reservations traces back to treaties and agreements between the tribes and the U.S. government. Each reservation has its own unique history and legal status, shaped by specific agreements and circumstances.
- Cultural Identity: The reservations serve as homelands for the federally recognized tribes of Arizona. They are centers of cultural preservation and revitalization, where traditions, languages, and spiritual practices are maintained and passed down through generations.
- Economic Impact: The reservations contribute to the state’s economy through various sectors, including tourism, gaming, and traditional industries. They provide employment opportunities and support local businesses, fostering economic development within the communities.
- Challenges and Opportunities: While the reservations offer cultural and economic benefits, they also face challenges such as poverty, unemployment, and limited access to resources. Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts between tribal governments, state and federal agencies, and community organizations.
In summary, the number “22 Indian reservations in Arizona” provides a snapshot of the historical, cultural, and economic significance of these territories within the state. Understanding this number and its implications enhances our comprehension of the complex relationship between Native American tribes and the wider society.
Tribes
The connection between “Tribes: 27 federally recognized tribes” and “how many Indian reservations in Arizona” lies in the historical and legal framework that governs the establishment and recognition of Indian reservations in the United States.
Indian reservations are territories set aside by the federal government for the exclusive use and occupancy of Native American tribes. The establishment of reservations is based on treaties, agreements, and laws that recognize the sovereignty and self-governance of federally recognized tribes.
In Arizona, there are 22 Indian reservations that are home to 27 federally recognized tribes. Each tribe has its own unique culture, language, and traditions, and each reservation has its own unique history and legal status.
The recognition of 27 federally recognized tribes in Arizona is significant because it acknowledges the distinct cultural and political identities of these tribes and their right to self-governance. It also provides a framework for the federal government to fulfill its treaty and trust obligations to these tribes.
The relationship between “Tribes: 27 federally recognized tribes” and “how many Indian reservations in Arizona” is essential for understanding the historical, cultural, and legal landscape of Native American communities in the state.
Location
The “Location: Spread across the state” aspect of Indian reservations in Arizona plays a significant role in understanding their distribution and impact within the state. Here are some key facets to explore:
- Geographic Diversity: Arizona’s Indian reservations are located in diverse geographic regions, from the arid deserts of the Sonoran Desert to the mountainous regions of the Colorado Plateau. This geographic diversity influences the cultural practices, economic activities, and environmental stewardship of each reservation.
- Historical Context: The current locations of Indian reservations are often tied to historical events and treaties between Native American tribes and the U.S. government. Understanding the historical context provides insights into the reasons behind the reservations’ locations and their significance to the tribes.
- Economic Impact: The location of Indian reservations can impact their economic development and opportunities. Proximity to urban centers or major transportation routes can influence tourism, gaming, and other industries on the reservations.
- Cultural Preservation: The geographic isolation of some reservations has contributed to the preservation of traditional cultures and languages. Distance from urban areas has allowed tribes to maintain their unique identities and practices, fostering cultural continuity.
In summary, the “Location: Spread across the state” aspect highlights the geographic diversity, historical significance, economic implications, and cultural preservation associated with Indian reservations in Arizona. Understanding the location of these reservations provides a deeper appreciation of their role in the state’s cultural and economic landscape.
Size
Indian reservations in Arizona vary significantly in size, ranging from small communities to vast landscapes. This variation in size has several implications and considerations within the context of “how many Indian reservations in Arizona”:
- Land Sovereignty and Autonomy: The size of a reservation can influence the level of land sovereignty and autonomy exercised by the tribe. Larger reservations often have more land and resources at their disposal, providing greater opportunities for self-governance and economic development.
- Population and Community Dynamics: The size of a reservation can impact its population density and community dynamics. Smaller reservations may have closer-knit communities with stronger social bonds, while larger reservations may have a more diverse population and a wider range of social and economic activities.
- Economic Opportunities and Challenges: The size of a reservation can influence its economic opportunities and challenges. Larger reservations may have more land available for economic development, such as agriculture, tourism, or natural resource extraction. However, smaller reservations may face greater challenges in attracting investment and developing sustainable economic activities.
- Cultural Preservation and Identity: The size of a reservation can play a role in cultural preservation and identity. Smaller reservations may have a stronger sense of cultural cohesion and shared traditions, while larger reservations may have a more diverse population and a wider range of cultural influences.
In summary, the “Size: Varying from small to large” aspect of Indian reservations in Arizona highlights the diverse nature of these communities and their unique circumstances. Understanding the size variations provides insights into land sovereignty, population dynamics, economic opportunities, and cultural preservation within the context of Indian reservations in the state.
History
The historical establishment of Indian reservations in Arizona through treaties and agreements is inextricably linked to the concept of “how many Indian reservations in Arizona.” Understanding this historical context is crucial for grasping the legal and political framework that governs the existence and recognition of these reservations.
Treaties and agreements between Native American tribes and the U.S. government played a pivotal role in defining the boundaries and legal status of Indian reservations. These agreements often involved land cessions, whereby tribes relinquished vast territories in exchange for the establishment of reservations. The reservations were intended to provide tribes with a permanent homeland and a degree of self-governance.
For instance, the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, signed in 1848, granted land rights to Native American tribes in Arizona and other southwestern territories. This treaty, along with subsequent agreements and executive orders, established the legal basis for many of the Indian reservations in the state.
Comprehending the historical context of treaties and agreements is essential for appreciating the legal framework that governs Indian reservations in Arizona. It sheds light on the complex relationship between tribes and the federal government and provides a foundation for understanding contemporary issues related to land rights, sovereignty, and self-governance.
Table: Treaties and Agreements Establishing Indian Reservations in Arizona
| Treaty/Agreement | Year | Established Reservations |
|---|---|---|
| Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo | 1848 | Various reservations in Arizona and the Southwest |
| Gadsden Purchase Treaty | 1853 | Additional reservations in southern Arizona |
| Fort Laramie Treaty | 1868 | Navajo and Hopi Reservations |
Culture
The rich and diverse cultures of the 27 federally recognized tribes in Arizona are deeply intertwined with the concept of “how many Indian reservations in Arizona.” Understanding this connection allows us to appreciate the importance of cultural preservation and its impact on the identity and well-being of Native American communities.
Indian reservations serve as havens for the preservation andof traditional languages, arts, crafts, and spiritual practices. Each tribe has its own unique cultural heritage, which is reflected in the distinct ceremonies, dances, songs, and stories that are passed down through generations.
Preserving these traditions is not only a matter of cultural pride but also a way of maintaining a connection to the past and ensuring the continuity of tribal identity. By safeguarding their cultures, Native American tribes can empower themselves and future generations.
Furthermore, the preservation of traditional cultures contributes to the overall cultural diversity of Arizona. The unique arts, crafts, and performances of Native American tribes enrich the state’s cultural landscape and provide valuable insights into the history and heritage of the region.
Table: Cultural Highlights of Indian Reservations in Arizona
| Tribe | Cultural Highlights |
|---|---|
| Navajo Nation | Traditional weaving, silversmithing, and sandpainting |
| Hopi Tribe | Kachina doll carving, pottery, and basketry |
| White Mountain Apache Tribe | Traditional basketry, beadwork, and storytelling |
| San Carlos Apache Tribe | Traditional Apache fiddle music and basketry |
| Yavapai-Apache Nation | Traditional basketry, pottery, and beadwork |
Economy
The economic contributions of Indian reservations in Arizona are closely tied to the concept of “how many Indian reservations in Arizona.” Understanding this connection is crucial for recognizing the economic impact and opportunities associated with these reservations.
Indian reservations in Arizona contribute significantly to the state’s economy through various industries, including tourism, gaming, and traditional arts and crafts.
Tourism: Many reservations offer cultural tours, historical sites, and scenic attractions, drawing tourists from around the world. This influx of visitors supports local businesses, creates jobs, and generates revenue for the reservations. Gaming: Gaming is a major economic driver for several Indian reservations in Arizona. Casinos and other gaming establishments provide employment opportunities, generate tax revenue, and contribute to the overall economic well-being of the reservations and surrounding communities. Traditional Arts and Crafts: Native American artisans create and sell exquisite pieces of art, jewelry, pottery, and textiles. These traditional crafts are not only cultural expressions but also sources of income for many Native American families.
The economic contributions of Indian reservations in Arizona extend beyond these core industries. Reservations also support agriculture, ranching, and other businesses, contributing to the state’s diverse economy.
Understanding the economic impact of Indian reservations in Arizona is essential for appreciating their role in the state’s economic landscape. This understanding can inform policy decisions, foster collaboration, and promote sustainable economic development in both Native American communities and the state as a whole.
Table: Economic Contributions of Indian Reservations in Arizona
| Industry | Impact |
|---|---|
| Tourism | Cultural tours, historical sites, scenic attractions |
| Gaming | Casinos, gaming establishments, employment opportunities |
| Traditional Arts and Crafts | Art, jewelry, pottery, textiles, cultural expression, income generation |
| Agriculture and Ranching | Food production, livestock, economic diversification |
Challenges
The connection between “Challenges: Facing issues such as poverty and unemployment” and “how many Indian reservations in Arizona” lies in the multifaceted issues confronting Native American communities within the state. Poverty and unemployment are prevalent challenges that significantly impact the well-being and economic opportunities of individuals and families residing on reservations.
Historically, Indian reservations have faced systemic barriers and limited access to resources, contributing to persistent poverty rates. Unemployment levels on reservations often exceed state and national averages due to a lack of job opportunities, limited infrastructure, and educational disparities. This situation can lead to a cycle of poverty, where limited economic prospects perpetuate financial struggles and hinder social mobility.
Addressing the challenges of poverty and unemployment on Indian reservations requires a comprehensive approach that involves collaboration between tribal governments, federal agencies, and non-profit organizations. Programs aimed at economic development, job training, and education are crucial for empowering Native American communities and creating sustainable economic opportunities.
Understanding the challenges faced by Indian reservations in Arizona is essential for developing effective policies and programs that promote economic growth and improve the lives of Native Americans in the state.
Table: Challenges and Impacts on Indian Reservations in Arizona
| Challenge | Impact |
|---|---|
| Poverty | Limited economic opportunities, financial struggles, social mobility barriers |
| Unemployment | Lack of job opportunities, limited infrastructure, educational disparities |
Sovereignty
Understanding “Sovereignty: Maintaining autonomy and self-governance” is crucial to grasping the concept of “how many Indian reservations in Arizona.” Indian reservations are distinct political entities with their own governments and laws, reflecting the sovereignty of the tribes that reside on them.
- Tribal Governments: Each Indian reservation has its own tribal government, responsible for governing its territory and providing essential services to its citizens. Tribal governments exercise authority over a range of issues, including law enforcement, education, healthcare, and economic development.
- Legal Systems: Indian reservations have their own legal systems, distinct from state and federal laws. These systems incorporate traditional tribal laws and customs, ensuring that justice is administered in a culturally appropriate manner.
- Economic Development: Tribes have the right to develop their economies and manage their natural resources. This includes establishing businesses, promoting tourism, and utilizing their lands for economic benefit.
- Cultural Preservation: Sovereignty allows tribes to preserve their unique cultures and traditions. They can establish and enforce cultural regulations, protect sacred sites, and promote language revitalization efforts.
Maintaining sovereignty is essential for the well-being and self-determination of Native American tribes in Arizona. It empowers them to govern their own affairs, preserve their cultural heritage, and pursue economic development opportunities.
Importance
The connection between “Importance: Preserving cultural heritage and contributing to the state’s identity” and “how many Indian reservations in Arizona” highlights the significance of these reservations in safeguarding and promoting Native American cultures while enriching Arizona’s unique identity.
Indian reservations serve as living museums, where traditional languages, art forms, ceremonies, and spiritual practices are passed down through generations. By preserving their cultural heritage, Native American tribes maintain a vital connection to their ancestors and ensure the continuity of their distinct identities.
Moreover, the presence of Indian reservations contributes to Arizona’s cultural diversity and tourism appeal. The state’s rich tapestry of Native American cultures attracts visitors from around the world, who come to experience the vibrant traditions, stunning landscapes, and historical sites found on the reservations.
Furthermore, Indian reservations play a vital role in fostering a sense of place and belonging for both Native Americans and non-Native residents. They serve as cultural hubs, where community members gather for powwows, festivals, and other events that celebrate their heritage and strengthen their bonds.
Table: Importance of Preserving Cultural Heritage and Contributing to the State’s Identity
| Aspect | Significance |
|---|---|
| Cultural preservation | Safeguarding traditional languages, art forms, ceremonies, and spiritual practices |
| Cultural diversity | Enriching Arizona’s cultural landscape and attracting visitors |
| Sense of place and belonging | Fostering a sense of community and connection to the land |
FAQs about Indian Reservations in Arizona
This section provides answers to frequently asked questions about Indian reservations in Arizona, offering valuable insights and clarifying common misconceptions.
Question 1: How many Indian reservations are in Arizona?
Answer: There are 22 Indian reservations in Arizona, home to 27 federally recognized tribes.
Question 2: Where are the Indian reservations located in Arizona?
Answer: Indian reservations in Arizona are spread across the state, from the arid deserts of the Sonoran Desert to the mountainous regions of the Colorado Plateau.
Question 3: What is the significance of Indian reservations?
Answer: Indian reservations serve as homelands for Native American tribes, preserving their unique cultures, traditions, and languages. They also contribute to Arizona’s cultural diversity and economic development.
Question 4: Are Indian reservations governed by the U.S. government?
Answer: Indian reservations are governed by their own tribal governments, which have the authority to make laws, provide essential services, and manage their territories.
Question 5: Can non-Native Americans live on Indian reservations?
Answer: In general, non-Native Americans cannot live on Indian reservations unless they are married to a tribal member or have specific permission from the tribe.
Question 6: How can I learn more about Indian reservations in Arizona?
Answer: You can visit the websites of individual tribes, attend cultural events on reservations, or contact the Arizona Indian Gaming Association for more information and resources.
Understanding these FAQs provides a deeper appreciation for the rich history, cultural significance, and contemporary realities of Indian reservations in Arizona.
Related article: Exploring the Cultural Heritage and Economic Impact of Indian Reservations in Arizona
Tips for Understanding Indian Reservations in Arizona
Exploring the topic of “how many Indian reservations in Arizona” involves delving into the rich history, cultural significance, and contemporary realities of these territories. Here are a few tips to enhance your understanding:
Tip 1: Recognize the Historical Context
Indian reservations in Arizona were established through treaties and agreements between Native American tribes and the U.S. government. Understanding this historical context provides a foundation for comprehending the legal and political framework that governs these reservations.
Tip 2: Respect Tribal Sovereignty
Indian reservations are distinct political entities with their own governments and laws. Respecting tribal sovereignty means acknowledging the authority of these governments and engaging with tribes in a respectful and cooperative manner.
Tip 3: Visit and Experience
The best way to learn about Indian reservations is to visit them in person. Attend cultural events, visit museums, and interact with tribal members to gain firsthand insights into their traditions and perspectives.
Tip 4: Support Native American Businesses
Indian reservations contribute to Arizona’s economy through various industries, including tourism, gaming, and traditional arts and crafts. Supporting Native American businesses not only helps these communities thrive but also allows you to appreciate their unique cultural expressions.
Tip 5: Engage with Local Organizations
There are many non-profit organizations and community groups dedicated to supporting Indian reservations in Arizona. Engaging with these organizations provides opportunities to learn more, volunteer, and contribute to their efforts.
Summary:
By following these tips, you can gain a deeper understanding of Indian reservations in Arizona, appreciate their cultural significance, and contribute to their well-being. Remember to approach these topics with respect, curiosity, and a willingness to learn from the diverse perspectives and experiences of Native American communities.
Exploring “How Many Indian Reservations in Arizona”
Our exploration of “how many Indian reservations in Arizona” has provided valuable insights into the historical, cultural, and contemporary aspects of these territories. We have learned that Arizona is home to 22 Indian reservations, each with its own unique history, culture, and government.
Understanding the concept of “how many Indian reservations in Arizona” requires an appreciation for the significance of these reservations in preserving Native American cultures, contributing to the state’s economy, and maintaining tribal sovereignty. By respecting tribal sovereignty, supporting Native American businesses, and engaging with local organizations, we can continue to foster a mutually beneficial relationship between Native American communities and the wider society.
As we move forward, it is important to recognize the ongoing challenges faced by Indian reservations in Arizona, such as poverty and unemployment. By working together, we can create a brighter future for all Arizonians, ensuring that the rich cultural heritage and economic contributions of Indian reservations continue to thrive.