California’s First People: A Tapestry of Tribes
California’s First People: A Tapestry of Tribes

California, the Golden State, is known for its sunny beaches, towering redwoods, and bustling cities. But before the Spanish arrived, before the gold rush, before the freeways and skyscrapers, California was home to a vibrant tapestry of Native American tribes. For thousands of years, these tribes thrived in this diverse landscape, their cultures as varied and rich as the land itself. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of California’s First People, exploring their unique stories and legacies.
From the Coast to the Mountains:
Related Articles: California’s First People: A Tapestry of Tribes
- Unveiling the Enduring Legacy: Indian Reservations in Montana
- Beyond The Strip: Unveiling The Hidden Gems Of Nevada’s Indian Reservations
- Uncover the Enchanting World of Sioux Indian Reservations in South Dakota
- Discover the Enchanting Tapestry of Native American Tribes in Montana
- Unveil the Tapestry of Native American Heritage with Our Indian Tribes in America Map
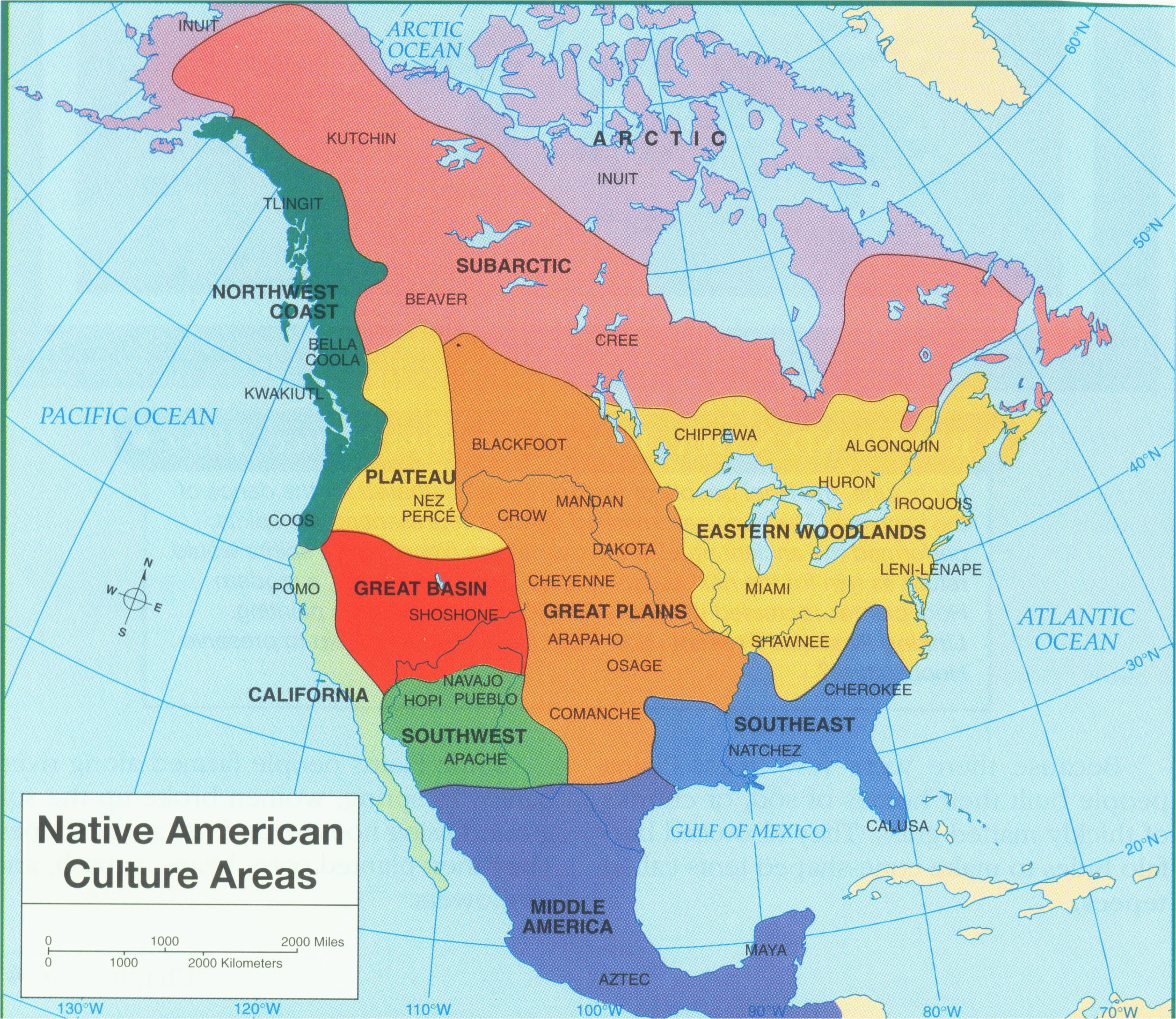
California’s geography is as varied as its indigenous peoples. From the rugged coastline to the towering Sierra Nevada mountains, the state’s diverse landscape supported a wide range of cultures.
-
Coastal Tribes: Along the Pacific coast, tribes like the Chumash, Tongva, and Yurok relied on the bounty of the ocean. They were skilled fishermen, crafting intricate tools and boats to navigate the waters. Their diet was rich in seafood, and their culture was deeply connected to the ocean’s rhythms.
-
Interior Tribes: In the vast interior, tribes like the Miwok, Mono, and Paiute adapted to a drier climate. They were skilled hunters and gatherers, utilizing the resources of the mountains and valleys. Their lives were closely tied to the seasons, their ceremonies and rituals celebrating the cycles of nature.

A Diversity of Languages and Traditions:
The tribes of California spoke over 100 distinct languages, making it one of the most linguistically diverse regions in North America. These languages weren’t just a means of communication; they were a reflection of their unique cultures and beliefs.
The Chumash of the central coast developed an elaborate system of pictographs, using symbols to record stories, events, and spiritual beliefs.
-
The Pomo of the north coast were renowned for their intricate basketry, using various materials and techniques to create stunning works of art.
-
The Yurok of the northwest coast were known for their elaborate dances and ceremonies, honoring their ancestors and the spirits of the natural world.

A Legacy Under Threat:
The arrival of European settlers in the 18th century marked a devastating turning point for California’s native peoples. Disease, displacement, and forced assimilation took a heavy toll, decimating their populations and eroding their cultural traditions.
-
Missionization: The Spanish established missions throughout California, forcing Native Americans to convert to Christianity and adopt European ways of life. This process often involved forced labor, separation from families, and the suppression of traditional practices.
-
Gold Rush: The discovery of gold in 1848 brought a flood of settlers to California, further displacing Native Americans and leading to violence and conflict. Many tribes were forced onto reservations, their lands and resources taken away.
Resilience and Revival:
Despite the challenges they faced, California’s Native American tribes have shown remarkable resilience. They have fought to preserve their languages, traditions, and cultural heritage, working to revitalize their communities and share their stories with the world.
-
Language Revitalization: Tribes across California are actively working to revive their ancestral languages, developing educational programs, creating dictionaries, and recording oral histories.
-
Cultural Preservation: Through museums, festivals, and community gatherings, Native Americans are sharing their rich cultural traditions with future generations, keeping their stories alive.
-
Political Advocacy: Tribes are fighting for recognition of their sovereignty, land rights, and treaty rights, working to ensure their voices are heard and their rights are protected.
The Importance of Understanding:
Learning about the history and culture of California’s Native American tribes is crucial for understanding the state’s rich history and the diverse tapestry of its people. By recognizing their contributions and struggles, we can build a more just and equitable future for all Californians.
Beyond the Golden State:
The stories of California’s Native Americans are part of a larger narrative of indigenous resilience and survival across North America. Their history reminds us of the importance of preserving cultural diversity, respecting ancestral lands, and acknowledging the injustices of the past.
Here are some things to consider as you continue your journey of learning about California’s First People:
-
Visit a Native American museum or cultural center: Immerse yourself in the history and culture of the tribes of California.
-
Attend a powwow or traditional ceremony: Experience the beauty and vibrancy of Native American traditions firsthand.
-
Support Native American-owned businesses and organizations: Help empower Native American communities and promote economic development.
-
Learn about the history of colonization and its impact on Native Americans: Understand the complex history of the state and the challenges faced by indigenous peoples.
FAQ About California’s Native American Tribes:
Q: How many Native American tribes were in California before European contact?
A: It is estimated that there were over 100 distinct tribes in California before European arrival, each with its own language, culture, and traditions.
Q: What are some of the major language families in California?
A: California’s Native American languages belong to several major language families, including Hokan, Penutian, Algonquian, and Uto-Aztecan.
Q: What are some of the most well-known California Native American tribes?
A: Some of the most well-known tribes include the Chumash, Tongva, Yurok, Miwok, Pomo, and Paiute.
Q: What are some of the challenges faced by California’s Native American tribes today?
A: Modern challenges include poverty, lack of access to healthcare and education, environmental degradation, and the ongoing struggle for recognition of their sovereignty and treaty rights.
Q: What can I do to support California’s Native American tribes?
A: You can support Native American-owned businesses, learn about their history and culture, donate to organizations that support their rights, and advocate for policies that promote their well-being.
By learning about the history and culture of California’s Native American tribes, we can honor their legacy and work towards a future where their voices are heard and their rights are respected. Let’s celebrate the rich tapestry of cultures that make California the vibrant and diverse state it is today.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into California’s First People: A Tapestry of Tribes. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!